How Microsoft anticipated wearables, machine learning and cognitive enhancement: Key Neurotech Patent #18
Let’s discuss today a fascinating patent assigned to Microsoft back in 2015. (As mentioned, we are featuring a foundational Pervasive Neurotech patent a day, from older to newer by issue date)
U.S. Patent No. 6,842,877: Contextual responses based on automated learning techniques.
- Assignee(s): Microsoft Corporation
- Inventor(s): James O. Robarts Eric L. Matteson
- Technology Category: Neurocognitive Training
- Issue Date: January 11, 2005
SharpBrains’ Take:
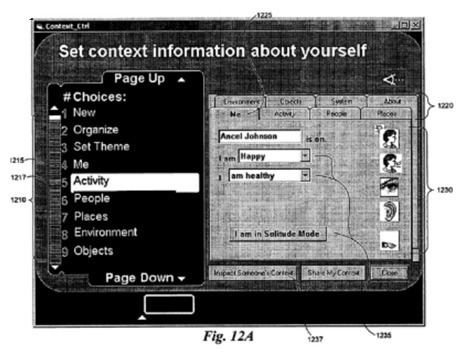
The ‘877 patent discloses wearable devices that incorporate techniques for user-feedback loops to automatically improve a system’s response, for example when the computing system identifies user’s needs and preferences through the use of sensing components, in a variety of environmental contexts.
Cognitive benefits may occur, when the automated response results in providing a template for user-improvement, such as using a person’s psychological profile under the Meyer-Briggs test to train an individual to be more outspoken if they are an introvert or be aware that, as an extrovert, they are spending too much time talking. Although the claims are focused on the adaptive learning aspect of the wearable device, this patent is a key non-invasive neurotechnology patent due to the intersection of the fast-growing wearable tech sector with the cognitive enhancement applications disclosed therein, the lengthy and detailed specification (with 48 illustration sheets and 31 pages of written material), and the application having received an average of 43 citations per year.
Abstract:
Techniques are disclosed for using a combination of explicit and implicit user context modeling techniques to identify and provide appropriate computer actions based on a current context, and to continuously improve the providing of such computer actions. The appropriate computer actions include presentation of appropriate content and functionality. Feedback paths can be used to assist automated machine learning in detecting patterns and generating inferred rules, and improvements from the generated rules can be implemented with or without direct user control. The techniques can be used to enhance software and device functionality, including self-customizing of a model of the user’s current context or situation, customizing received themes, predicting appropriate content for presentation or retrieval, self-customizing of software user interfaces, simplifying repetitive tasks or situations, and mentoring of the user to promote desired change.
Illustrative Claim 41. A wearable computing system configured to improve automated responses to a current context for a user, the current context being represented by a plurality of context attributes that each model an aspect of the context, multiple defined contextual situations each specifying values for at least one of the context attributes, multiple automated responses being associated with the defined contextual situations, comprising:
- a first component that is configured to repeatedly, receive an indication of current context information that includes current values for each of at least some of the plurality of context attributes, determine one of the defined contextual situations that matches the indicated current context information, determine one of the automated responses that is associated with the one defined contextual situation, receive an indication from the user of an alternate automated response, and store an indication of the indicated current context information and the alternate automated response; and
- a second component that is configured to automatically detect a relationship between an identified contextual situation and one of the alternate automated responses based on that alternate automated response being previously indicated by the user and to create an association between the identified contextual situation and the one alternate automated response so that the one alternate automated response can in the future be provided to the user for that contextual situation.
 To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.
To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.