Testing and training cognitive ability: Key Neurotech Patent #16
Today we are featuring a key 2003 patent assigned to Cognifit ltd — fascinating to reflect how the brain training field has evolved in 14 years! (As mentioned, we are featuring a foundational Pervasive Neurotech patent a day, from older to newer by issue date)
U.S. Patent No. 6,632,174: Method and Apparatus for testing and training cognitive ability
- Assignee(s): Cognifit ltd
- Inventor(s): Shlomo Breznitz
- Technology Category: Neurocognitive Training
- Issue Date: October 14, 2003
SharpBrains’ Take:
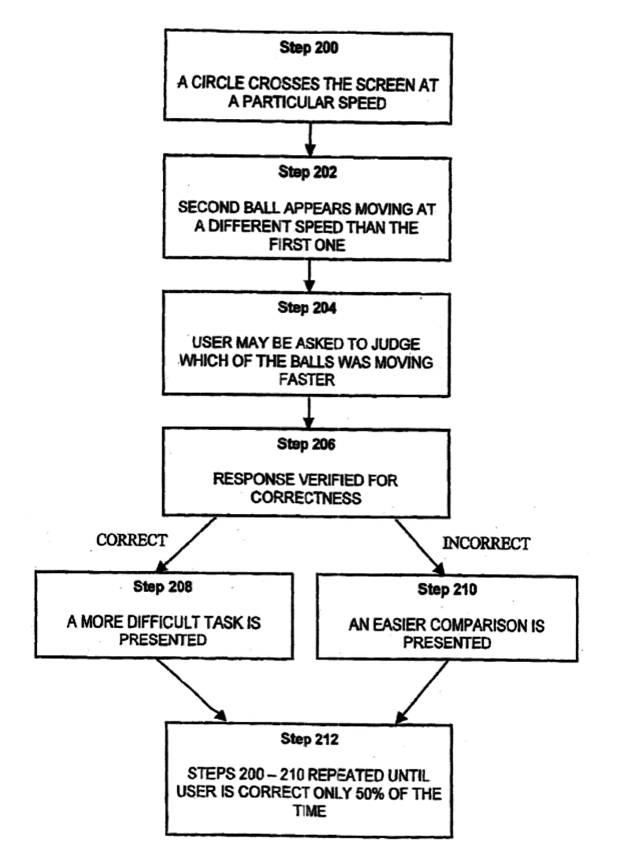
The Detailed Description of the ‘174 patent accurately contextualises the teachings of the patent when it recites “the present invention utilizes analysis, mental exercise and intervention in an attempt to increase cognitive abilities, improve speed of reaction, and train both functional cognitive attentional, perceptual, and linguistic abilities and various aspects of memory.” In other words, the ‘174 patent provides general purpose approaches for cognitive training. The ‘174 patent also includes broad independent claims (a total of seven) though it is uncertain how some limitations may impact claim scope (e.g., “receiving a motion input” recited in claim 1). Interestingly, techniques are described for breaking cognitive assessments/tasks into discrete skills and segments for precision training of areas that require additional attention or present bottlenecks, thereby establishing a mechanism for deep or deliberate training. While the specification is somewhat brief (with only seven illustration sheets and seven pages of written material), the broad claim set and general purpose cognitive training techniques are amongst the factors contributing to identifying the ‘174 patent as a key non-invasive neurotechnology patent.
Abstract:
A method for testing and/or training cognitive ability, including the steps of testing a preliminary cognitive level of a user and receiving results representative therefrom. According to the results, the cognitive level may then be broken up into separate discrete cognitive skills, and one or more tasks may be created, each task related to each of the separate discrete cognitive skills. The one or more tasks may then be presented to the user and so that a current cognitive level of the user is re-tested, and results representative therefrom are received. This process may be repeated at least one time.
Illustrative Claim 1. A method for diagnosing and training cognitive ability of a user, the method comprising:
- presenting a stimulus
- receiving a motion input generally in response to said stimulus
- analyzing cognitive skills of said motion input for a diagnosis to selecting one or more tasks to train said cognitive skills
 To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.
To learn more about market data, trends and leading companies in the digital brain health space –digital platforms for brain/ cognitive assessment, monitoring and enhancement– check out this market report. To learn more about our analysis of 10,000+ patent filings, check out this IP & innovation neurotech report.