Posts Tagged ‘academic-achievement’
Study: Early-childhood attention skills help predict long-term academic success better than IQ, socioemotional skills, or socioeconomic status
—– Which early child characteristics predict long-term academic achievement and educational attainment? Research has focused on the role of early academic skills, learning enhancing behaviors, and socioemotional competencies as precursors of academic success. Identifying the relative contribution of each to children’s long-term academic achievement is important as it can inform the skills on which early…
Read MoreStudy: Neonatal MRI scans of preterm children can help predict cognitive and academic problems, and guide early interventions
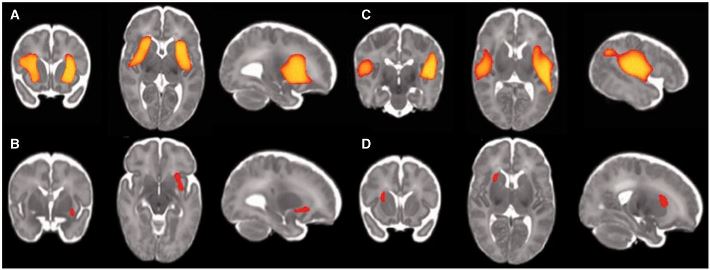
Predicting future cognition in preterm children with MRI (Oxford University Press blog): “In the wake of the development of advanced neonatal intensive medical care, more and more children born preterm manage to beat the previously tough odds…While this is one of the success stories of modern medicine, long-term follow-up of premature-born pediatric cohorts show that…Many children…
Read MoreTo improve academic outcomes, children with ADHD need both medication and non-medication treatments
. Academic problems are extremely common in children with ADHD, and often the issue that leads to referral for an ADHD evaluation. Academic outcomes can be measured in 2 different ways — academic achievement and academic performance — and both are compromised in children with ADHD. Academic achievement refers to the information and skills that children…
Read MoreStudy: Dyslexia not related to intelligence. Implications for discrepancy model?
NIH-funded study finds dyslexia not tied to IQ (NIH press release): — “Regardless of high or low overall scores on an IQ test, children with dyslexia show similar patterns of brain activity, according to researchers supported by the National Institutes of Health. The results call into question the discrepancy model — the practice of classifying…
Read MoreDoes ADHD medication treatment in childhood increase adult employment?
Although ADHD used to be considered a disorder of childhood, follow-up studies indicate that between 30% and 60% of children with ADHD continue to experience symptoms and impairment in adulthood. And, even when ADHD symptoms decline over time, many individuals continue to experience significant impairment in important areas of functioning. For example, children with ADHD have
Read MoreShould Social-Emotional Learning Be Part of Academic Curriculum?
The Secret to Success New research says social-emotional learning helps students in every way. — by Daniel Goleman Schools are beginning to offer an increasing number of courses in social and emotional intelligence, teaching students how to better understand their own emotions and the emotions of others. It sounds warm and fuzzy, but it’s a trend…
Read More